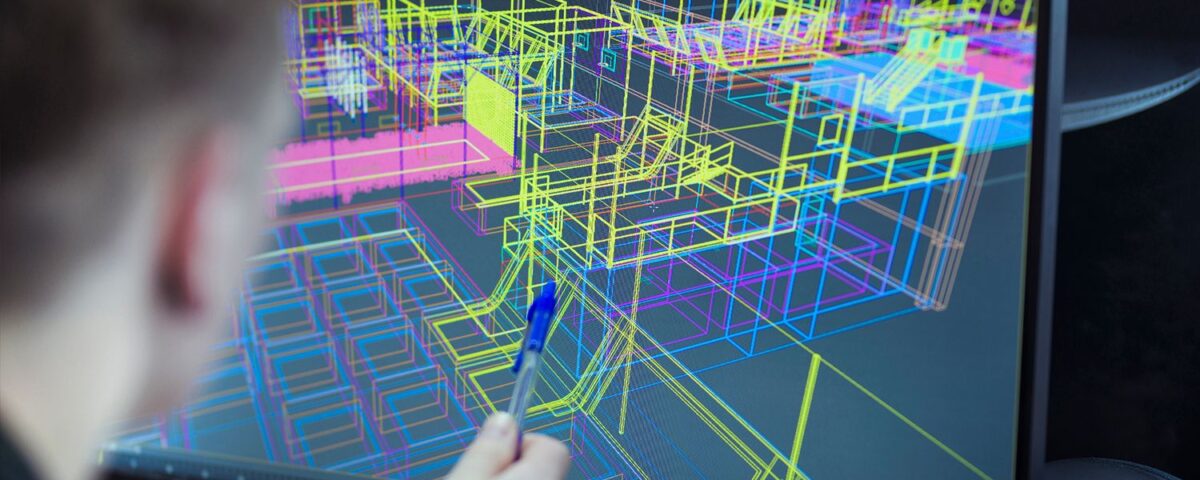
Exploring the World of 3D Modeling: From Concept to Creation
The Ultimate Guide to Infographics: Crafting Visual Stories
May 22, 2024
Mastering Adobe Photoshop: A Comprehensive Guide
May 22, 2024Exploring the World of 3D Modeling: From Concept to Creation
Introduction to 3D Modeling
3D modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects or scenes. It involves manipulating vertices, edges, and polygons to generate realistic or stylized 3D models. These models can be used in various industries, including animation, gaming, architecture, product design, and visual effects.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!The Importance of 3D Modeling
3D modeling plays a crucial role in many fields for several reasons:
- Visualization: 3D models provide a visual representation of concepts, designs, and ideas, making them easier to understand and evaluate.
- Prototyping: 3D models can be used to create prototypes and mockups for testing purposes before manufacturing or construction begins.
- Animation and Entertainment: In the entertainment industry, 3D models are used to create characters, environments, and special effects for movies, television shows, and video games.
- Architectural Visualization: Architects and designers use 3D models to visualize buildings, interiors, and landscapes, allowing clients to see how the final project will look before construction begins.
- Product Design: 3D modeling is widely used in product design and development to create detailed digital prototypes that can be refined and optimized before production.
Types of 3D Modeling
Polygonal Modeling
Polygonal modeling is the most common type of 3D modeling, where objects are created by manipulating vertices, edges, and faces. It’s suitable for creating organic shapes, characters, and environments.
NURBS Modeling
Non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) modeling uses mathematical curves and surfaces to create smooth, precise shapes. It’s often used in automotive design, industrial design, and product visualization.
Subdivision Modeling
Subdivision modeling starts with a simple polygonal mesh and subdivides it to create smoother and more detailed surfaces. It’s ideal for creating complex organic shapes and characters.
Digital Sculpting
Digital sculpting simulates traditional sculpting techniques in a digital environment. Artists use specialized software to sculpt virtual clay, allowing for intuitive and organic creation of characters and creatures.
Parametric Modeling
Parametric modeling uses mathematical parameters and constraints to create models that can be easily modified and adapted. It’s commonly used in engineering, architecture, and mechanical design.
The 3D Modeling Process
Conceptualization
The process begins with conceptualization, where artists or designers brainstorm ideas and sketches for the 3D model. This stage involves defining the purpose, scope, and visual style of the project.
Modeling
Once the concept is finalized, the modeling phase begins. Artists use 3D modeling software to create the basic shapes and structures of the model, refining and detailing as needed.
Texturing
Texturing involves adding surface details and materials to the model. This includes applying textures, colors, and shaders to create realistic or stylized appearances.
Rigging and Animation
For animated models, rigging is the process of adding a skeleton or armature to the model, allowing it to be animated. Animation involves creating keyframes and movements to bring the model to life.
Lighting and Rendering
Lighting and rendering are crucial for creating realistic or visually appealing images. Artists set up virtual lights and cameras, adjust settings, and render the final images or animations.
Post-Processing
Post-processing involves enhancing the final images or animations through techniques such as compositing, color correction, and special effects.
Tools for 3D Modeling
Autodesk Maya
Autodesk Maya is a comprehensive 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software used by professionals in the film, television, and gaming industries.
Blender
Blender is a free and open-source 3D creation suite that offers modeling, animation, rigging, rendering, and compositing capabilities.
ZBrush
ZBrush is a digital sculpting software used for creating high-detail models and characters. It’s widely used in the gaming and entertainment industries.
Cinema 4D
Cinema 4D is a user-friendly 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software known for its intuitive interface and powerful features.
Autodesk 3ds Max
Autodesk 3ds Max is a popular software for modeling, animation, and rendering, particularly in architecture, product design, and visualization.
Best Practices for 3D Modeling
Plan and Research
Before starting a project, gather references, sketches, and inspiration to guide your modeling process. Planning helps streamline workflow and avoid unnecessary revisions.
Keep it Low-Poly
Optimize your models by keeping polygon counts low wherever possible. This improves performance and efficiency, particularly for real-time applications like games and simulations.
Focus on Detailing
Pay attention to small details and surface imperfections to make your models more realistic and visually appealing.
Experiment and Practice
Experiment with different techniques, tools, and software to expand your skills and creativity. Practice regularly to improve your modeling abilities and efficiency.
Seek Feedback
Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or online communities to improve your work. Constructive criticism can help identify areas for improvement and growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring Topology
Poor topology can result in deformation issues, shading errors, and difficulty in animation. Pay attention to edge flow and topology to ensure smooth and accurate deformations.
Overcomplicating Models
Avoid adding unnecessary details or complexity to your models. Keep them simple and focused on the main idea or purpose.
Neglecting Texturing and Lighting
Texturing and lighting are essential for creating realistic and visually appealing renders. Don’t overlook these aspects of the 3D modeling process.
Skipping Rigging and Animation
For animated models, rigging and animation are essential steps. Skipping these steps can limit the usability and versatility of your models.
Conclusion
3D modeling is a versatile and powerful tool used in various industries for visualizing, prototyping, and creating digital content. By understanding the different types of 3D modeling, the modeling process, tools, and best practices, you can create high-quality models that meet the needs of your projects. Whether for entertainment, design, or engineering, 3D modeling offers endless possibilities for creativity and innovation.
For more information: www.ecbinternational.com